Descriptive epidemiology of 287 confirmed cases of new coronavirus infection reported by the national epidemiological surveillance of infectious disease system (NESID) and active epidemiological surveillance (as of March 9, 2020)
Posted date 2020/3/17
On February 1, 2020, new coronavirus infectious disease (COVID-19) was added as a designated infectious disease under the Infectious Diseases Control Law, article 6 in paragraph 8, which required doctors to immediately report diagnosed COVID-19 cases to the public health center in their jurisdiction. These reported cases were aggregated through the national epidemiological surveillance of infectious diseases (NESID) system. Additionally, active epidemiological investigation could then be conducted, as stipulated in the Infectious Diseases Control Law, article 15.
The primary sources of data in this report were lab-confirmed COVID-19 cases reported through NESID and active epidemiological investigations, as of March 9. Data in NESID were aggregated from reporting by local public health centers. Daily data in active epidemiological investigation by local public health centers were aggregated by teams from the Novel Coronavirus Response Headquarters at the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (MHLW). This updated report provides additions to the report published on February 24 (https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/en/2019-ncov-e/2484-idsc/9473-2019-ncov-08-e-2.html). As data collection is ongoing, this report may be revised or updated accordingly in the future. It should also be noted that there are cases in which there may have been delayed reporting or case notification not yet completed. As such, there may be a difference in the number of cases reviewed in this report versus those under active investigation by MHLW. It is expected that this difference will be resolved in the future, but please note that there may be a difference.
Based on data reported as of March 9, 2020 by both NESID and MHLW’s active epidemiologic investigations, there were 287 lab-confirmed COVID-19 cases.
The gender ratio was 1.2:1, higher for males, with 159 males and 128 females total.
The median age was 66 years (age range 4-91), with age of distribution of 3 cases in the 0-9 age range (1.0%), 2 in the 10-19 age range (0.7%), 17 in the 20-29 age range (5.9%), 18 in the 30-39 age range (6.3%), 26 in the 40-49 age range (9.1%), 48 in the 50-59 age range (16.7%), 54 in the 60-69 age range (18.8%), 91 in the 70-79 age range (31.7%), 27 in the 80-89 age range (9.4%), and one in the 90+ age range (0.3%). Approximately 60% of cases were identified in those over 60 years of age.
The nationality of cases were 200 cases from Japan, 21 from the United States, 18 from Australia, 11 from China, 8 from Canada, 6 from the Philippines, 5 from India, 5 from Hong Kong, 4 from Indonesia, 2 from Thailand, 2 from New Zealand, 1 from Colombia, 1 from Romania and 3 cases with unconfirmed nationality.
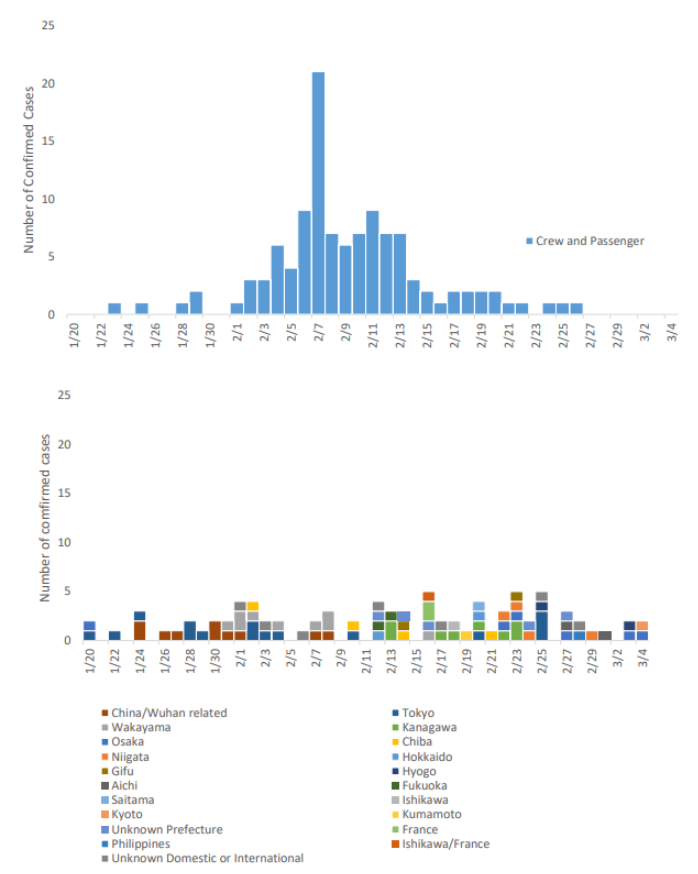
Possible routes of infection identified were 188 cases originating from ship-based travel (crew and passengers), 11 cases with travel history to China or Wuhan city, 18 in Tokyo, 11 in Wakayama, 10 in Kanagawa, 8 in Osaka, 5 in Chiba, 4 in Niigata, 2 in Hokkaido, 2 in Ishikawa, 2 in Gifu, 2 in Aichi, 2 in Hyogo, 2 in Fukuoka, 1 in Saitama, 1 in Nagano, 1 in Kyoto, 1 in Kumamoto, 5 in an unknown Japanese prefecture, 2 with travel history to France, 1 with travel history to the Philippines, 1 in linkage with Ishikawa and France, and 7 with unknown infection transmission route.
Figure 1 shows the epidemic curve of 200 cases with known dates of symptom onset, from January 20 - March 4, 2020. The remaining 87 cases did not have symptom onset day recorded and were excluded. As shown, the confirmed ship-related COVID 19 cases of crew and passengers peaked on February 7 and confirmed cases with travel history to China or Wuhan city were higher in January, with the other cases having a sporadic spread over the given timeframe.
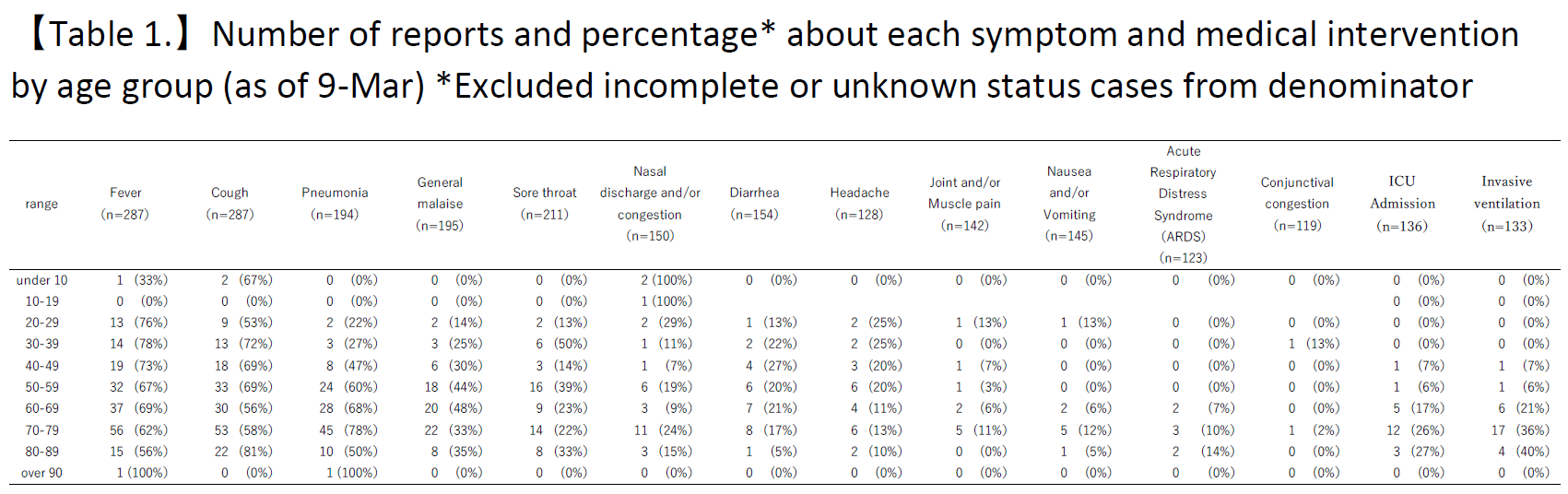
In table 1, the number of reported cases by age group for each symptom and medical intervention is shown. From the time when the case was reported until March 9, the main symptoms identified were fever 188/287 (66%), cough 180/287 (63%), pneumonia 121/194 ( 62%), general malaise 79/195 (41%), sore throat 58/211 (27%), nasal discharge and/or congestion 30/150 (20%), diarrhea 29/154 (19%), headache 25/128 (20%), joint and/or muscle pain 10/142 (7%), nausea and/or vomiting 9/145 (6%), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) 7/123 (6%), and conjunctival congestion 2/119 (2%). Please note that the change in denominators was due to the exclusion of a case from the total if there was no information provided for that symptom or if it was unknown.
For medical interventions used, there were 22/136 (16%) intensive care unit (ICU) admissions and 29/133 (22%) invasive ventilations (including endotracheal intubation). Other interventions used included extracorporeal membrane oxygenator (ECMO) in 9 cases, with 1 in their 40s, 2 in their 60s, 5 in their 70s, and 1 in their 80s. Please note that the change in denominators was due to the exclusion of a case from the denominator if there was no information provided for that medical intervention or if it was unknown, which may have led to an overestimation of the percentages.
Regarding severe cases requiring medical interventions, the presence of co-morbidities was analyzed. For the 22 cases requiring ICU admission: 10 had known co-morbidities, 2 had no co-morbidities, 10 had unknown status/no information for co-morbidities. For the 29 cases that required invasive ventilation: 15 cases had known co-morbidities, 1 had no co-morbidities, and 13 had unknown status for co-morbidities. For the 9 cases that required ECMO: 6 had known co-morbidities and 3 had unknown status/no information for co-morbidities.
At the time of COVID-19 case diagnosis, 71 cases (25%) were reported as asymptomatic cases. Out of the reported 71 asymptomatic cases, 6 cases had symptom onset dates provided which were either before the date of diagnosis or the same as the date of diagnosis. Of the remaining 65 reported asymptomatic cases, there were 22 symptomatic cases included without symptom onset dates provided and 11 symptomatic cases with symptom onset dates after the date of diagnosis. Among asymptomatic cases with symptom onset dates after the report day, 5 cases required invasive ventilation (such as endotracheal intubation) and 2 of those 5 required ECMO. As of March 9, there were 32 asymptomatic cases (11%).
As of March 9, the health outcomes of the 287 cases analyzed were 3 deaths (1%) and 115 hospital discharges (40%). The mean value (standard deviation) of the hospitalization period for 102 cases with known hospitalization admission and discharge dates was 14.3 days (± 5.2 days).
This report summarized a portion of the overall lab-confirmed cases in Japan, as reported by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare on March 9: 472 domestic cases, 15 returnee cases on charter flights, and 696 cruise ship crew and passenger cases. We will continue to collect, analyze, and feedback information on COVID-19 in Japan in order to understand the trends and the severity of the disease, and to reflect them in measures.
We would like to extend our sincere gratitude to the local government officials and public health centers for their continued cooperation in reporting COVID-19 cases during the outbreak as part of the NESID system.
【Figure 1.】Confirmed COVID-19 Cases, by date of onset, from Jan-20 to Mar-4, the information source are National Epidemiological Surveillance of Infectious Disease (NESID) and Active epidemiological investigation, as of Mar-9 (n=200)Erratum
March 30, 2020 Percentages for "General malaise" in Table 1 have been corrected.