| |
13. 世界のブルーリ潰瘍の現状は?
30ヵ国以上から年間約5,000人の新患の報告がありますが、実数はさらに上回ると考えられています。
WHOは1998年にBuruli Ulcer Global Initiativeを発足させ、日本でも国立感染症研究所ハンセン病研究センターを中核的センターとし、症例の集積や検査、疫学的検討、治療法、潰瘍の治療法などの検討を行っています。
14. これからの課題は?
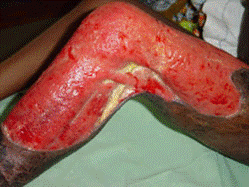
ブルーリ潰瘍は熱帯皮膚病と考えられていましたが、日本にも存在する感染症です。患者数は近年増加していますが、早期診断・治療することで後遺症を残さず治癒に導くことが可能です。
今後ブルーリ潰瘍の感染様式、特に感染源やベクターの解明を行い、感染ルートを明らかにして予防につなげる必要があります。また早期発見のために皮膚科医を中心に啓発に努め、さらにアジア諸国と連携をもって、各国でのブルーリ潰瘍の発見をサポートすべきです。
15. ブルーリ潰瘍に関する問合せ先:
石井則久 Norihisa ISHII このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。 (現・国立療養所多磨全生園)
宮本友司 Yuji MIYAMOTO このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。
国立感染症研究所ハンセン病研究センター
〒189-0002 東村山市青葉町4-2-1
Tel:042-391-8211 FAX: 042-391-8210
https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/ja/from-lab/489-lrc/9558-lrc-top.html
16. 主な文献:
教科書
- 石井則久:皮膚抗酸菌症テキスト. 金原出版, 東京, 2008.
総説
- 石井則久、他:深い潰瘍を形成する新たな非結核性抗酸菌感染症 Mycobacterium shinshuense感染症. 臨床皮膚科 64(増刊): 8-12, 2010.
- 四津里英、他:アフリカの抗酸菌症が日本にも-ブルーリ潰瘍-. MBデルマ183: 41-49, 2011.
- Nakanaga K, et al.: Nineteen cases of buruli ulcer diagnosed in Japan from 1980 to 2010. J Clin Microbiol 49: 3829-3836, 2011.
- 石井則久、他:ブルーリ潰瘍. 日本臨床皮膚科医会雑誌 29: 376-383, 2012.
- Yotsu RR, et al.: Buruli ulcer and current situation in Japan: a new emerging cutaneous Mycobacterium infection. J Dermatol 39: 587-593, 2012.
- Nakanaga K, et al.: Laboratory procedures for the detection and identification of cutaneous non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections. J Dermatol 40: 151-159, 2013.
- Nakanaga K, et al.: Buruli ulcer and mycolactone-producing mycobacteria. Jpn J Infect Dis 66: 83-88, 2013.
- 濱田利久: ブルーリ潰瘍. 日本皮膚科学会雑誌 124: 23-26, 2014
- Yotsu RR, et al.: Revisiting buruli ulcer. J Dermatol 42: 1033-1041, 2015.
- 四津里英、他: 潰瘍を伴う抗酸菌症-Buruli潰瘍とその病理-. 病理と臨床 33: 862-868, 2015.
- 菅原万里子、他: ブルーリ潰瘍のすべて. MB Derma 242: 115-122, 2016.
日本の症例
- Tukamura M, Mikoshiba H: A new mycobacterium which caused skin infection. Microbiol Immunol 26: 951-955, 1982.
- 御子柴 甫、他:Mycosbacterium ulcerans類似菌による非定型抗酸菌症の1例. 日本皮膚科学会雑誌92: 557-565, 1982.
- 今田英明、他:Mycobacterium shinshuense により生じたBuruli潰瘍に類似した難治性肘頭部潰瘍の 1 例. 整形外科 59: 1440-1445, 2008.
- 鈴木智子、他:“M. ulcerans subsp. shinshuense”による皮膚潰瘍. 皮膚病診療30: 145-148, 2008.
- Funakoshi T, et al.: Intractable ulcer caused by Mycobacteriumshinshuense: successful identification of mycobacterium strain by 16S ribosomal RNA 3'-end sequencing. Clin Exp Dermatol 34: e712-e715, 2009.
- Kondo M, et al.: Leg ulcer caused by Mycobacterium ulcerans ssp.shinshuense infection. Int J Dermatol 48: 1330-1333, 2009.
- Watanabe T, et al.: Buruli ulcer caused"Mycobacterium ulcerans subsp.shinshuense". Eur J Dermatol 20: 809-810, 2010.
- 湊 はる香、他: 多剤併用療法が奏効したブルーリ潰瘍 (Mycobacterium ulcerans subsp. shinshuense 感染症)の1例. 皮膚臨床53, 1219-1220, 1301-1304, 2011.
- 加畑大輔、他:Mycobacterium ulcerans subsp. shinshuenseによるBuruli潰瘍の1例. 日皮会誌121: 3337-3342, 2011.
- Matsumura Y, et al.: A case of buruli ulcer due to Mycobacterium ulcerans ssp. shinshuense with distal cutaneous involvement and synovitis. J Dermatol 39: 80-83, 2012.
- Onoe H, et al.: Buruli ulcer accompanied by pain in a Japanese patient. J Dermatol 39: 869-870, 2012.
- 濱田利久:Buruli潰瘍. 皮膚病診療 35: 665-668, 2013.
- 梅林芳弘、他:秋田県で発生したBuruli潰瘍. 皮膚病診療35: 669-672, 2013.
- Ohtsuka M, et al.: Buruli ulcer caused by mycobacterium ulcerans subspshinshuense: A rare case of familial concurrent occurrence and detection of insertion sequence 2404 in Japan. JAMA Dermtol 150: 64-67, 2013.
- Takahashi T, et al.: Mapping biopsy procedure on management of severe buruli ulcer due to Mycobacterium ulcerans, subspecies shinshuense. JAMA Dermatol 150: 669-671, 2014.
- Miyamoto Y, et al.: Two cases of Buruli ulcer in Japanese brothers. J Dermatol 41: 771-772, 2014.
- Murase C, et al.: Buruli ulcer successfully treated with negative-pressure wound therapy. JAMA Dermatol 151: 1137-1139, 2015.
- 三井田 博、他: 両側前腕に病変が多発したブルーリ潰瘍の1例. 臨皮 71: 71-76, 2017.
- 藤澤正男、他: 結核ともハンセン病とも違う皮膚抗酸菌症: ブルーリ潰瘍. Visual Dermatol 16: 346-348, 2017.
- Hayami T, et al: Mapping biopsy for Buruli ulcer self-medicated with occlusive dressing. J Dermatol 45: 72-75, 2017.
日本人による主な研究論文など
- Mwanatambwe M, et al.: Clinico- histopathological findings of Buruli ulcer. Jap J Lepr 69: 93-100, 2000.
- 中永和枝、他:Mycobacterium ulcerans感染マウスに対するrifalazilおよびrifampicinの発症阻止効果の比較. 結核 79: 333-339, 2004.
- Goto M, et al.: Nerve damage in Mycobacterium ulcerans- infected mice: probable cause of painlessness in buruli ulcer. Am J Pathol 168: 805-811, 2006.
- 中永和枝、他: Mycobacterium shinshuense と Mycobacterium leprae の分子生物学的診断法の有用性. 日本ハンセン病学会雑誌76: 245-250, 2007.
- Nakanaga K, et al.: "Mycobacterium ulcerans subsp. shinshuense" isolated from a skin ulcer lesion: identification based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing. J Clin Microbiol: 45:3840-3843, 2007.
- En J, et al.: Mycolactone is responsible for the painlessness ofMycobacterium ulcerans infection (Buruli Ulcer) in a murine study. Infect Immun 76: 2002-2007, 2008.
- 圓純一郎、他:ブルーリ潰瘍(Mycobacterium ulcerans感染症)の神経傷害におけるmycoloctoneの役割. 日本ハンセン病学会雑誌 80: 5-10 , 2011.
- Nakanaga K, et al.: Laboratory procedures for detection and identification of cutaneous non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections. J Dermatol 40: 151-159, 2013.
- Nakanaga K, et al.: Buruli ulcer and mycolactone-producing mycobacteria. Jpn J Infect Dis 66: 83-88, 2013.
- Luo Y, et al.: Detection of Mycobacterium ulcerans subsp. shinshuense DNA from a water channel in familial Buruli ulcer cases in Japan. Future Microbiol 10: 461-469, 2015.
- Watanabe M, et al.: Protective effect of a dewaxed whole-cell vaccine against Mycobacterium ulcerans infection in mice. Vaccine 33: 2232-2239, 2015.
- Sugawara M, et al.: Exploration of a standard treatment for Buruli ulcer through a comprehensive analysis of all cases diagnosed in Japan. J Dermatol 42: 588-595, 2015.
- 四津里英、他: 潰瘍を伴う抗酸菌症―Buruli潰瘍とその病理―. 病理と臨床 33: 862-868, 2015.
WHOの本・資料
- Kingsley A, et al.: Buruli ulcer: Mycobacterium ulcerans infection. World Health Organization, Global Buruli Ulcer Initiative, 2000.
- World Health Organization: Provisional guidance on the role of specific antibiotics in the management of Mycobacterium ulcerans disease (Buruli ulcer). World Health Organization, Geneva, 2004.
- World Health Organization: Buruli ulcer: progress report, 2004-2008. Weekly Epideniological Record 83( No. 17): 145-156, 2008.
- World Health Organization: Treatment of Mycobacterium ulceransdisease (Buruli ulcer). World Health Organization, Geneva, 2010.
感染源・ベクターの研究
- Johnson PDR, et al.: Mycobacterium ulcerans in mosquitoes captured during outbreak of Buruli ulcer , southeastern Australia. Emerg Infect Dis 13: 1653-1660, 2007.
- Portaels F, et al.: First cultivation and characterization of Mycobacterium ulcerans from the environment. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2: e178, 2008.
- Williamson HR, et al.: Distribution of Mycobacterium ulcerans in Buruli ulcer endemic and non-endemic aquatic sites in Ghana. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2: e205, 2008.
- Stinear T, Johnson PDR: First isolation of Mycobacterium ulcerans from an aquatic environment: the end of a 60-year search?. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2: e216, 2008.
- Merritt RW, et al.: Ecology and transmission of Buruli ulcer disease: a systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 4: e911, 2010.
毒素(マイコラクトン)の研究
- Pimsler M, et al.: Immunosuppressive properties of the soluble toxin fromMycobacterium ulcerans. J Infect Dis 157: 577-580, 1988.
- George KM, et al.: Partial purification and characterization of biological effects of a lipid toxin produced by Mycobacterium ulcerans. Infect Immun 66: 587-593, 1988.
- George KM, et al.: Mycolactone: a polyketide toxin from Mycobacterium ulcerans required for virulence. Science 283: 854-857, 1999.
- Sarfo FS, et al.: Detection of mycolactone A/B in Mycobacterium ulcerans-infected human tissue. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 4: e577, 2010.
- Pidot SJ, et al.: Mycobacterium ulcerans and other mycolactone- Producing mycobacteria should be considered a single species. PLoS 4: e663, 2010.
- Spangenberg T, Kishi Y: Highly sensitive, operationally simple, cost/time effective detection of the mycolactones from the human pathogenMycobacterium ulcerans. Chem Commun (Camb) 46: 1410-1412 , 2010.
- Jackson KL, et al.: Scalable and efficient synthesis of the mycolactone core. Tetrahedron 66: 2263-2272, 2010 .
- Nakanaga K, et al: Buruli ulcer and mycolactone-producing mycobacteria. Jpn J Infect Dis 66: 83-88, 2013.
- En J, et al: Mycolactone cytotoxicity in Schwann cells could explain nerve damage in Buruli ulcer. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 11: e0005834, 2017.
|
|
|---|